PROBLEM #108 Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Topics: Array, Divide and Conquer, Tree, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree
Problem Statement
Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
Example 1:
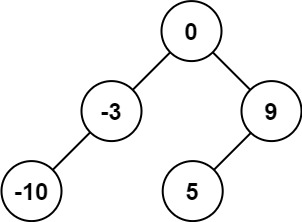
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted.

Example 2:
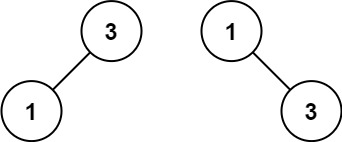
Input: nums = [1,3]
Output: [3,1]
Explanation: [1,null,3] and [3,1] are both height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
SOLUTIONS
Recursive
Intuition
In a BST, a key property is that all nodes in its left subtree have values less than the root node’s value, and all nodes in its right subtree have values greater than the root node’s value. Therefore, when constructing a BST from a sorted array, the middle element of the sorted array is always selected as the root node, and elements to the left and right of the middle element are assigned to the left and right subtrees, respectively.
Approach
- If the input sorted array is empty, return None because there’s no tree to construct.
- Find the middle element of the sorted array and use it as the root node.
- Recursively construct the left subtree with elements to the left of the middle element and the right subtree with elements to the right of the middle element.
- Return the root node.
Complexity
- Time complexity: O(N), where N is the number of elements in the sorted array.
- Space complexity: O(log N) due to the recursive call stack and auxiliary space used in each recursive call.
C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* createBST(vector<int> nums, int s, int e) {
if (s > e) return NULL;
int mid = s + (e - s) / 2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = createBST(nums, s, mid - 1);
root->right = createBST(nums, mid + 1, e);
return root;
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
int s = 0;
int e = nums.size() - 1;
return createBST(nums, s, e);
}
};
Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] num) {
if (num.length == 0) {
return null;
}
TreeNode head = helper(num, 0, num.length - 1);
return head;
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] num, int low, int high) {
if (low > high) {
return null;
}
int mid = low + (high-low)/2;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(num[mid]);
node.left = helper(num, low, mid - 1);
node.right = helper(num, mid + 1, high);
return node;
}
}